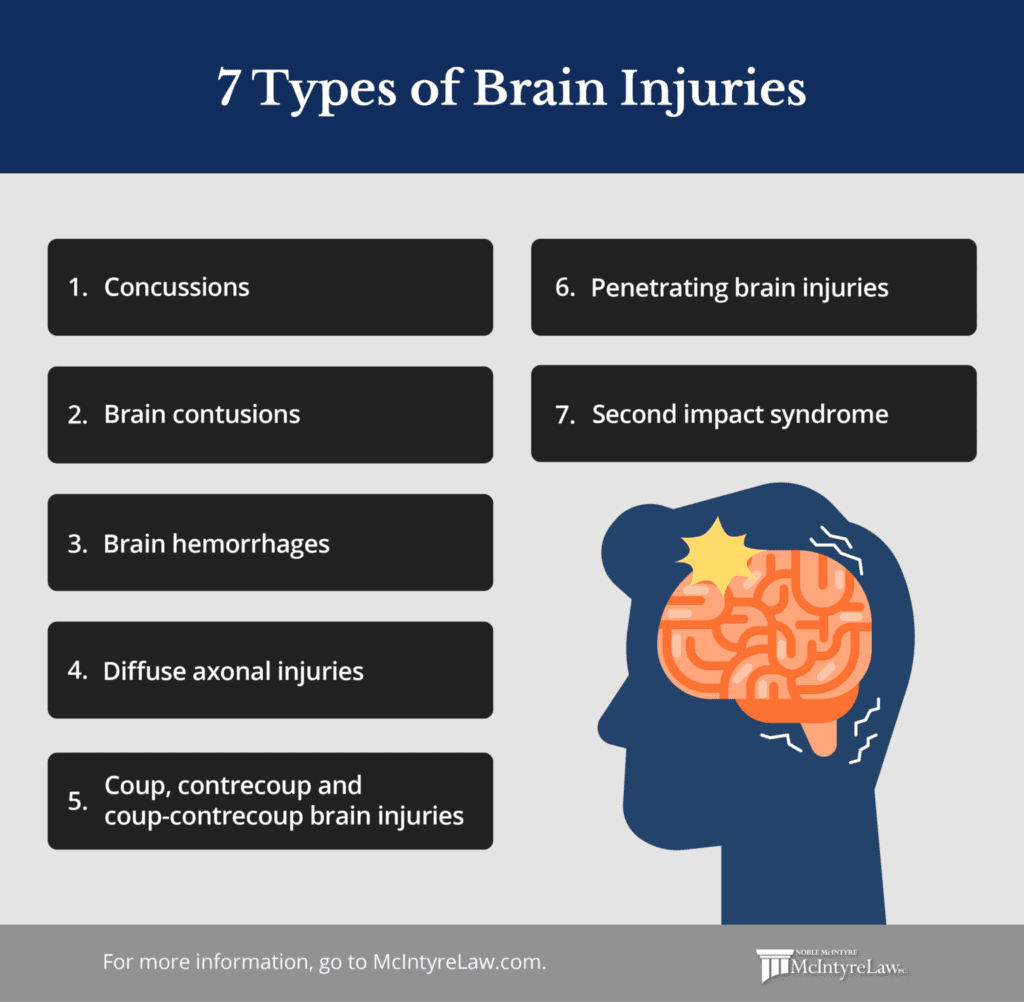
Jump to section:
- Concussions
- Brain contusions
- Brain hemorrhages
- Diffuse axonal injuries
- Coup, contrecoup and coup-contrecoup brain injuries
- Penetrating brain injuries
- Second impact syndrome
1. Concussions
Concussions are a common form of mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a sudden jolt, blow, or impact to the head or body, resulting in the rapid movement of the brain within the skull. Unlike more severe TBIs, concussions do not typically involve structural brain damage visible on imaging tests. Instead, they disrupt the brain’s normal functioning temporarily, leading to a range of cognitive, physical, and emotional symptoms.
Common causes of concussions include sports-related injuries, falls, motor vehicle accidents, or any event where the head experiences a significant force. Symptoms of a concussion can vary widely from person to person and while most concussions resolve with appropriate rest and recovery, repeated concussions or failure to manage them properly can lead to more severe complications and prolonged recovery periods.
What to expect after a concussion
If you are diagnosed with a concussion, you may experience a variety of symptoms that can manifest immediately or in the hours or days following the injury. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, confusion, memory difficulties, difficulty concentrating, sensitivity to light or noise, fatigue, and changes in mood or emotions, such as irritability or anxiety. Some individuals may also report sleep disturbances and balance problems. It is important to note that not all symptoms may be present in every case, and the severity and duration of symptoms can vary widely from person to person.
Most individuals with a concussion experience a gradual improvement of symptoms over a period of days to weeks. In many cases, the acute symptoms may resolve within the first week or two, but some individuals may continue to experience lingering effects that persist for several weeks or even months. Complete recovery can take longer, particularly in cases of more severe concussions or if there is a history of previous head injuries. Rest and appropriate management are essential during the recovery period to allow the brain to heal and prevent further complications. It is important for individuals who have sustained a concussion to follow the guidance of their healthcare providers, including gradual return-to-activity protocols, to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Treatment for concussions and post-concussion syndrome
Most treatments for concussions revolve around physical and cognitive in order to allow the brain sufficient time to heal. This involves limiting activities that could exacerbate symptoms, such as intense physical exertion, screen time, and mentally demanding tasks. Close monitoring of symptoms by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine when it is safe to gradually reintroduce activities. Medications may be recommended to manage symptoms like headaches and proper hydration as well as a well-balanced diet can contribute to the healing process.
In some cases, you may experience prolonged symptoms that extend beyond the typical recovery period, a condition known as post-concussion syndrome (PCS). PCS is characterized by the persistence of concussion-related symptoms for weeks, months, or even years after the initial injury. Symptoms of PCS can include ongoing headaches, dizziness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, irritability, anxiety, and changes in sleep patterns. It’s important to recognize that PCS is a complex condition with a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and overall well-being. If someone is experiencing prolonged symptoms consistent with post-concussion syndrome, you should seek medical attention to properly evaluate and manage this condition.
2. Brain contusions
Brain contusions are injuries that commonly occur in automobile accidents. These injuries involve bruising on the brain that can have a devastating impact on a person’s life. It is crucial for individuals to understand what this injury is and what treatment options are available.
The word contusion is used to describe a type of closed head injury that is common among victims of motor vehicle accidents. By definition, a contusion is a bruise on the brain. Bruising on the brain indicates that blood has leaked out from veins and mixed with tissues in the brain. These injuries are typically found in cortical tissues, which are the areas inside the skull that are near sharp ridges.
These injuries typically occur in situations where victims sustain bumps, blows, or jolts to the head or body during a motor vehicle accident. These sudden movements can cause the head and brain to shift quickly back and forth. Even in cases where the skull does not fracture, individuals can suffer contusions from the banging of their brain against their skull.
Symptoms of brain contusions
Individuals who suffer these types of traumatic brain injury often exhibit various symptoms. Generally, sufferers will feel confused, tired, emotional, or even upset following a motor vehicle accident. In some cases, particularly when more severe contusions or present, brain swelling can appear. When brain swelling is present, victims often experience symptoms like:
- Memory loss
- Problems paying attention
- Emotional disturbances
- Problems with motor skills
- Light sensitivity
- Inability to concentrate
- Lack of coordination
- Numbness
- Inability to understand speech
- Inability to speak
Brain contusion treatments and recovery timeline
When head injuries occur, individuals often undergo imaging tests like CT Scans and MRIs to diagnose and monitor damage, while surgeries like clot removal and skull fracture repair might be required. Medications and induced comas could be used to reduce swelling and alleviate symptoms. The high costs of such care make it vital for victims to seek restitution through legal avenues, especially when injuries result from negligent drivers.
Recovery periods vary; some experience relief within a day, while most cases take longer. The most rapid recovery typically occurs within the first three months post-injury, and brain contusion recovery may complete within six months. However, some cases extend beyond a year, especially for individuals over 40, who generally recover more slowly. Adequate rest during the post-hospitalization period is crucial for victims’ recovery.
3. Brain hemorrhages
Brain hemorrhages are serious medical conditions characterized by the abnormal bleeding within the brain tissue or the surrounding spaces. This bleeding can be caused by a variety of factors, including traumatic injuries, ruptured blood vessels, high blood pressure, blood clotting disorders, or underlying medical conditions. The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary depending on its location, severity, and the underlying cause, but common signs include sudden severe headaches, neurological deficits like numbness or weakness, confusion, altered consciousness, and in severe cases, coma. If gone untreated, a brain hemorrhage can lead to increased pressure within the skull, potentially damaging brain cells and affecting normal brain function.
Common causes of brain hemorrhages
Brain hemorrhages can arise for a variety of reasons, often stemming from underlying medical conditions or traumatic events. Understanding the various causes of a brain hemorrhage is essential for both medical professionals and the general public, as it helps to identify risk factors, promote prevention, and facilitate timely intervention. Here are some of the common causes that can contribute to the occurrence of brain hemorrhages:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Chronic high blood pressure can weaken blood vessel walls over time, making them more susceptible to rupture and causing intracranial bleeding.
- Cerebral Aneurysms: A cerebral aneurysm is a weakened, bulging area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to a subarachnoid hemorrhage, causing bleeding into the space surrounding the brain.
- Traumatic Brain Injuries: Severe head trauma, such as from accidents or falls, can cause blood vessels to rupture within the brain, leading to intracerebral or subdural hemorrhages.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Conditions that affect the blood’s ability to clot properly, such as hemophilia or certain medications, can increase the risk of spontaneous bleeding within the brain.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): AVMs are abnormal tangles of blood vessels in the brain that can rupture and cause bleeding. They are often congenital and can remain asymptomatic until a hemorrhage occurs.
4. Diffuse axonal injuries
One of the most serious and catastrophic injuries an individual can have is Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI). It is both a fatal and a common form of brain injury. More importantly, it is a leading cause of death for those individuals afflicted with traumatic brain injury and seen in approximately half of those who have had a serious head injury.
It is characterized by lesions that are spread throughout the brain. These lesions occur in the white matter tissue of the brain and are the result of considerable damage. Diffuse Axonal injury symptoms are most often seen lurking behind the scenes for individuals that are in a vegetative state due to a head injury.
After an accident where one’s head is significantly impacted, a coma can result. An individual in a coma that has DAI has a 90% chance of never coming out. If one can beat these incredible odds, they tend to regain their consciousness in a very impaired state.
Causes of diffuse axonal injuries
It takes as a very significant cutting force directed at the head that has rapid acceleration or deceleration of the brain within the skull. That is to say, the brain is severely slammed back and forth in the skull. Common accidents that can cause this rapid movement leading to Diffuse Axonal Injury include:
- Automobile accidents
- Physical violence
- Sports injuries
- Falls
- Shaken baby syndrome/child abuse
When this violent back and forth occurs the brain is displaced within the skull and the axons are disrupted. Axons work to send messages between the neurons. The tissues sliding over each other in a shearing motion cause the tears and lesions associated with this prognosis. These lesions lead to unconsciousness and ultimately brain cell death and swelling of the organ.

How diffuse axonal injuries are treated
Unfortunately, there is not a standard treatment that can be used for this type of traumatic brain injury. A medical professional’s main focus is on trying to reduce pressure and stop pressure from continuing to build inside the skull. If the pressure is unable to be halted, further damage will result. Steroids are often employed to help with inflammation as intensive forms of treatment like surgery will not work.
If recovery is an option, long-term rehabilitation with a team of medical support staff is required to be able to have any chance of success. Many facets of life are affected and focused therapy such as speech, occupational, physical, adaptive training, recreational, and cognitive counseling are needed. Even with a team of providers, the outlook on life-long medical issues is prominent. Sadly, the majority of victims do not recover and come out of their vegetative state.
Those that suffer DAI will not be able to return to normal daily life before their injuries occurred if at all.
5. Coup, contrecoup and coup-contrecoup brain injuries
Brain injuries can have lasting effects, changing an injured party’s life infinitely in just a moment’s time. A coup and contrecoup brain injury are named based on the point of impact of the injury.
- Coup brain injuries. A coup is an injury to the brain that occurs on the same hemisphere of the brain where the hit occurred.
- Contrecoup brain injuries. A contrecoup injury is a brain injury that occurs on the opposite area where the impact occurred. These injuries cause the brain to hit the skull against the opposite wall.
- Coup-contrecoup brain injuries. In injuries where the brain hits both sides of the skull it is called a coup-contrecoup brain injury. Often, these injuries are misdiagnosed and only one side of the brain is treated.
Treatment and recovery timeline for coup, contrecoup and coup-contrecoup brain injuries
Following any head injury, seeking prompt treatment is crucial as damage may not be immediately visible. Visible symptoms of coup-contrecoup injuries include loss of consciousness, confusion, headaches, nausea, and difficulty speaking. While there is no specific cure for a concussion, recommended remedies for recovery include rest, fluids, pain medication, and ice for swelling. Coup-contrecoup injuries, often more severe, might also require prescription medication or neurosurgery to reduce swelling.
Typically, individuals with mild concussions are advised rest and recovery for around seven to 10 days, though the duration can extend significantly depending on the injury’s severity. Some may experience post-concussion syndrome, where symptoms worsen over time, leading to longer recovery periods of months. Returning to daily activities should consider both physical and cognitive strain, especially with high-cognitive tasks like reading, social interactions, or screen use. While the long-term goal is returning to work, it’s vital to prioritize full healing, which may involve temporary work accommodations such as transportation assistance, flexible hours, breaks, or environmental modifications.
6. Penetrating brain injuries
A penetration brain injury can also be called an open head injury and it happens when an object pierces the skull and enters into the brain matter. High-velocity projectiles such as bullets cause this type of traumatic brain injury. While bullets are the most common, even low-velocity objects like heavy weighted and very sharp items can do the same. Knives, machetes, hatchets, and the like can also cause penetration brain injury.
Skull fractures, where a piece of the skull bone breaks off and enters the brain causing damage, is a very common cause of this serious traumatic brain injury. When this happens, the victim will have damage done to the area where the bone fragment entered, on either the right or left side of the brain affecting its functioning. Accidents that can cause fractures in the skull may include smashing the head, car accidents, falls, and sports accidents to name a few.
Damages associated with penetrating brain injuries
Damages that come with high-velocity objects penetrating the brain often have long-term destructive results than their low-velocity counterparts. Bullets have been shown to cause death in approximately 92% of their targets. For those that survive, there will be some amount of brain damage. In some cases, it can be mild, but in other cases, it can be very severe. Whether an individual is shot on purpose or by accident, the results are the same when a bullet smashes through the skull and enters the brain.
Treatment for penetrating brain injuries
Treatment severity is based on the traumatic brain injury’s extent and location, along with the resulting symptoms. Initial priority involves stabilizing the victim and stopping the bleeding. Neurosurgery might be required, involving removal of foreign objects or skull fragments and, in some cases, part of the skull to accommodate swelling. Draining bleeding through burr holes and monitoring pressure, temperature, and oxygen levels follows.
Post-stabilization, ongoing monitoring is essential with the use of devices inserted into the brain. Seizures might arise, requiring anti-seizure medication, while opioids are often used for pain management. Rehabilitation is also often required to restore health and functionality. A multidisciplinary team of physical therapists, occupational therapists, neurologists, and psychologists aids recovery and supports the patient’s journey toward regaining normalcy.
7. Second impact syndrome
Second Impact Syndrome (SIS) is a rare but extremely serious condition that occurs when an individual sustains a second traumatic brain injury before fully recovering from a previous one. This rapid occurance of brain injuries can lead to a dangerous and often fatal outcome. SIS is thought to result from the brain’s inability to regulate blood flow properly after the initial injury, causing rapid swelling and increased intracranial pressure. This can lead to severe brain dysfunction and even death within minutes of the second impact.
The effects of Second Impact Syndrome can be devastating, not only for the individual experiencing it but also for their loved ones. Due to the rapid and severe nature of SIS, there is often little time for medical intervention, and the consequences can be immediate. Survivors of SIS may experience severe neurological deficits leading to a profound impact on their daily life and making the simplest tasks challenging or even impossible.
Symptoms of second impact syndrome
The consequences of SIS can escalate rapidly, leading to severe brain dysfunction and life-threatening outcomes. Understanding the array of symptoms associated with SIS is vital for identifying warning signs and seeking immediate medical attention to prevent further injury. Some symptoms of Second Impact Syndrome include:
- Cardiac irregularities or sudden cardiac arrest
- Rapid and severe deterioration of consciousness
- Dilated pupils or unequal pupil size (anisocoria)
- Loss of control over bodily movements, including muscle weakness or paralysis
- Profound confusion and disorientation
- Agitation or restlessness
- Seizures or convulsions
- Difficulty breathing or irregular breathing patterns
What are the most common causes of a TBI?
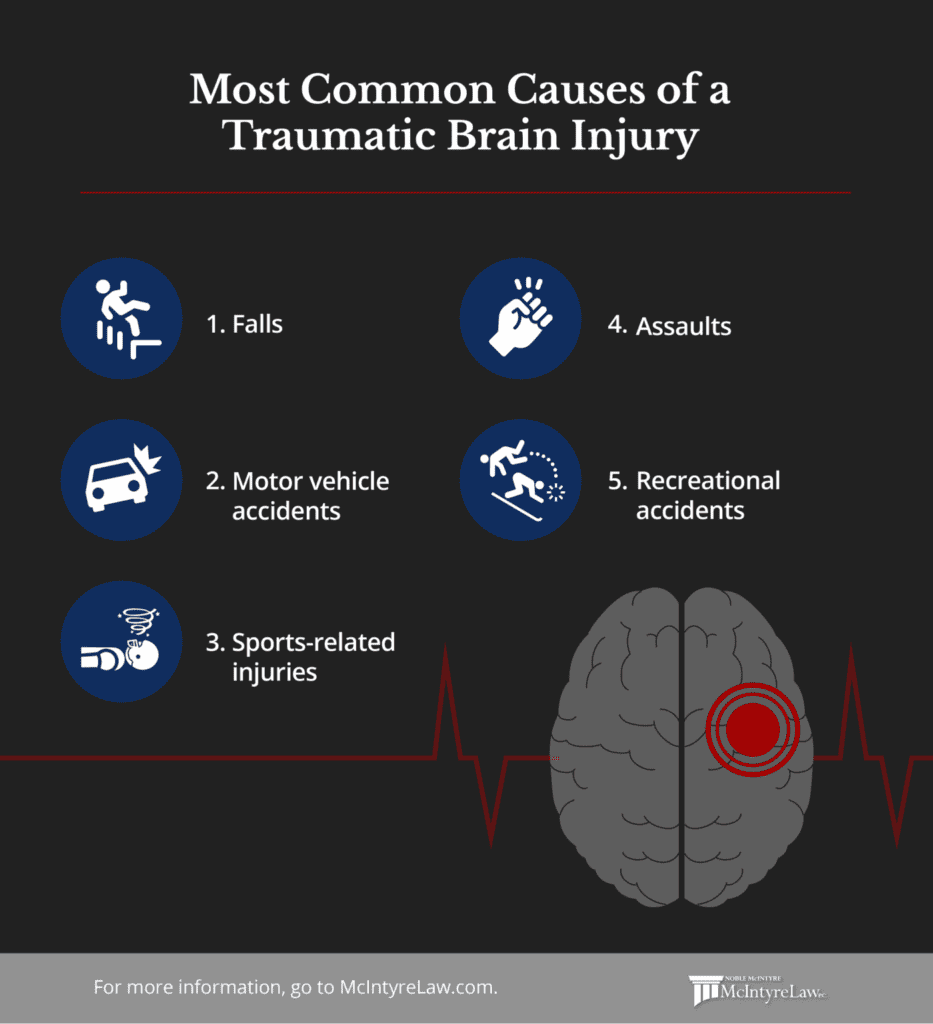
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) can occur due to a wide range of accidents and incidents, often resulting from sudden injuries to the head. These injuries can vary in severity from mild concussions to severe, life-altering trauma. Common causes of TBIs are diverse and can include falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports-related collisions and more. Here are some of the typical scenarios that can lead to traumatic brain injuries:
- Falls. Falls can lead to traumatic brain injuries when the impact to the head is significant enough to cause the brain to move within the skull. This sudden movement can result in brain tissue damage, bruising, or bleeding, ranging from mild concussions to more severe injuries like intracranial hemorrhages or skull fractures.
- Motor vehicle accidents. Car accidents put you at an increased risk of direct head impact which can cause TBIs. A bad collision can result in head trauma, leading to concussions, contusions, or more severe injuries that affect brain function and overall well-being.
- Sports-related injuries. Sports-related injuries can disrupt the brain’s normal functioning, causing concussions or other forms of head trauma that range in severity and can result in cognitive, physical, and emotional impairments.
- Assaults. Intentional blows to the head and other forms of assault can result in direct trauma to the brain. The forceful impact can cause various degrees of brain damage, including concussions, contusions, or even more severe injuries, depending on the nature and severity of the assault.
- Recreational accidents. Recreational accidents from activities like diving and skiing can result in collisions or impacts that transmit force to the head. The forceful contact can cause brain tissue damage, leading to concussions, contusions, or more severe injuries that affect cognitive, physical, and emotional function.
Costs associated with treating a traumatic brain injury
Treating a traumatic brain injury (TBI) over an individual’s lifetime can incur significant financial costs. Medical expenses such as hospitalization, surgeries, imaging tests, and rehabilitation can quickly accumulate. In addition, the long-term consequences of TBIs may lead to ongoing medical care, therapy, and support services to manage cognitive, physical, and psychological impairments. These costs include not only medical treatments but also expenses related to adjustments in daily living, assistive devices, home modifications, and specialized education or training.
The impact of TBIs on an individual’s quality of life can extend beyond personal suffering, affecting family members and caregivers who also bear emotional and financial burdens. For these reasons, seeking compensation for injuries is necessary. Legal actions, insurance claims, and pursuing avenues for financial restitution can help alleviate the financial strain and ensure that you receive the necessary support for comprehensive recovery to enhance the long-term well-being of both the affected individual and their support network.
When to contact an attorney following a traumatic brain injury
Recovering from this type of traumatic brain injury is often a long-term process and comes with chronic pain as well as a decrease in one’s quality of life. Most victims do not regain full control of their bodies and their lives the way they had before their accidents. Inability to concentrate, mood swings, loss of control over fine motor skills, and chronic migraines are just a few of the lasting symptoms that a victim may face. The costs for medical treatments and therapies, the emotional distress, and the trauma that can result from this type of injury adds up.
An experienced personal injury attorney at McIntyre Law will fight to hold those responsible for your damages accountable. The brain injury lawyers at McIntyre Law have your best interests in mind and we know that in order for you to be successful in recovery, you need the highest amount of compensation possible. Our team of personal injury lawyers is available to discuss your situation at 405-917-5200, call us today.